USB Configuration
Device Descriptors
The bcdUSB field reports the highest version of USB the device supports. The value is in binary coded decimal with a format of 0xJJMN where JJ is the major version number, M is the minor version number and N is the sub minor version number. e.g. USB 2.0 is reported as 0x0200, USB 1.1 as 0x0110 and USB 1.0 as 0x0100.
The bDeviceClass, bDeviceSubClass and bDeviceProtocol are used by the operating system to find a class driver for your device. Typically only the bDeviceClass is set at the device level. Most class specifications choose to identify itself at the interface level and as a result set the bDeviceClass as 0x00. This allows for the one device to support multiple classes.
The bMaxPacketSize field reports the maximum packet size for endpoint zero. All devices must support endpoint zero.
The idVendor and idProduct are used by the operating system to find a driver for your device. The Vendor ID is assigned by the USB-IF.
The bcdDevice has the same format than the bcdUSB and is used to provide a device version number. This value is assigned by the developer.
Three string descriptors exist to provide details of the manufacturer, product and serial number. There is no requirement to have string descriptors. If no string descriptor is present, a index of zero should be used.
bNumConfigurations defines the number of configurations the device supports at its current speed.
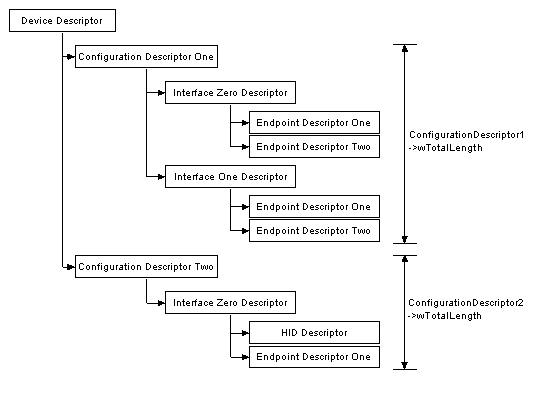
The device descriptor of a USB device represents the entire device. As a result a USB device can only have one device descriptor. It specifies some basic, yet important information about the device such as the supported USB version, maximum packet size, vendor and product IDs and the number of possible configurations the device can have. The format of the device descriptor is shown below.
| Offset | Field | Size | Value | Description |
| 0 | bLength | 1 | Number | Size of the Descriptor in Bytes (18 bytes) |
| 1 | bDescriptorType | 1 | Constant | Device Descriptor (0x01) |
| 2 | bcdUSB | 2 | BCD | USB Specification Number which device complies too. |
| 4 | bDeviceClass | 1 | Class | Class Code (Assigned by USB Org) If equal to Zero, each interface specifies it’s own class code If equal to 0xFF, the class code is vendor specified. Otherwise field is valid Class Code. |
| 5 | bDeviceSubClass | 1 | SubClass | Subclass Code (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 6 | bDeviceProtocol | 1 | Protocol | Protocol Code (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 7 | bMaxPacketSize | 1 | Number | Maximum Packet Size for Zero Endpoint. Valid Sizes are 8, 16, 32, 64 |
| 8 | idVendor | 2 | ID | Vendor ID (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 10 | idProduct | 2 | ID | Product ID (Assigned by Manufacturer) |
| 12 | bcdDevice | 2 | BCD | Device Release Number |
| 14 | iManufacturer | 1 | Index | Index of Manufacturer String Descriptor |
| 15 | iProduct | 1 | Index | Index of Product String Descriptor |
| 16 | iSerialNumber | 1 | Index | Index of Serial Number String Descriptor |
| 17 | bNumConfigurations | 1 | Integer | Number of Possible Configurations |
Example (USB webcam : ususb -v)
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 2232:1010
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 2.00
bDeviceClass 239 Miscellaneous Device
bDeviceSubClass 2 ?
bDeviceProtocol 1 Interface Association
bMaxPacketSize0 64
idVendor 0x2232
idProduct 0x1010
bcdDevice 0.19
iManufacturer 1 123
iProduct 2 WebCam SC-13HDN10939N
iSerial 0
bNumConfigurations 1
Configuration Descriptors
A USB device can have several different configurations although the majority of devices are simple and only have one. The configuration descriptor specifies how the device is powered, what the maximum power consumption is, the number of interfaces it has. Therefore it is possible to have two configurations, one for when the device is bus powered and another when it is mains powered. As this is a "header" to the Interface descriptors, its also feasible to have one configuration using a different transfer mode to that of another configuration.
Once all the configurations have been examined by the host, the host will send a SetConfiguration command with a non zero value which matches the bConfigurationValue of one of the configurations. This is used to select the desired configuration.
| Offset | Field | Size | Value | Description |
| 0 | bLength | 1 | Number | Size of Descriptor in Bytes |
| 1 | bDescriptorType | 1 | Constant | Configuration Descriptor (0x02) |
| 2 | wTotalLength | 2 | Number | Total length in bytes of data returned |
| 4 | bNumInterfaces | 1 | Number | Number of Interfaces |
| 5 | bConfigurationValue | 1 | Number | Value to use as an argument to select this configuration |
| 6 | iConfiguration | 1 | Index | Index of String Descriptor describing this configuration |
| 7 | bmAttributes | 1 | Bitmap | D7 Reserved, set to 1. (USB 1.0 Bus Powered) D6 Self Powered D5 Remote Wakeup D4..0 Reserved, set to 0. |
| 8 | bMaxPower | 1 | mA | Maximum Power Consumption in 2mA units |
When the configuration descriptor is read, it returns the entire configuration hierarchy which includes all related interface and endpoint descriptors. The wTotalLength field reflects the number of bytes in the hierarchy.
bNumInterfaces specifies the number of interfaces present for this configuration.
bConfigurationValue is used by the SetConfiguration request to select this configuration.
iConfiguration is a index to a string descriptor describing the configuration in human readable form.
bmAttributes specify power parameters for the configuration. If a device is self powered, it sets D6. Bit D7 was used in USB 1.0 to indicate a bus powered device, but this is now done by bMaxPower. If a device uses any power from the bus, whether it be as a bus powered device or as a self powered device, it must report its power consumption in bMaxPower. Devices can also support remote wakeup which allows the device to wake up the host when the host is in suspend.
bMaxPower defines the maximum power the device will drain from the bus. This is in 2mA units, thus a maximum of approximately 500mA can be specified. The specification allows a high powered bus powered device to drain no more than 500mA from Vbus. If a device loses external power, then it must not drain more than indicated in bMaxPower. It should fail any operation it cannot perform without external power.
QEMU struct DescConfig definition
struct USBDescConfig {
uint8_t bNumInterfaces;
uint8_t bConfigurationValue;
uint8_t iConfiguration;
uint8_t bmAttributes;
uint8_t bMaxPower;
/* grouped interfaces */
uint8_t nif_groups;
const USBDescIfaceAssoc *if_groups;
/* "normal" interfaces */
uint8_t nif;
const USBDescIface *ifs;
};
Interface Descriptors
bInterfaceNumber indicates the index of the interface descriptor. This should be zero based, and incremented once for each new interface descriptor.
bAlternativeSetting can be used to specify alternative interfaces. These alternative interfaces can be selected with the Set Interface request.
bNumEndpoints indicates the number of endpoints used by the interface. This value should exclude endpoint zero and is used to indicate the number of endpoint descriptors to follow.
bInterfaceClass, bInterfaceSubClass and bInterfaceProtocol can be used to specify supported classes (e.g. HID, communications, mass storage etc.) This allows many devices to use class drivers preventing the need to write specific drivers for your device.
iInterface allows for a string description of the interface.
The interface descriptor could be seen as a header or grouping of the endpoints into a functional group performing a single feature of the device. The interface descriptor conforms to the following format,
| Offset | Field | Size | Value | Description |
| 0 | bLength | 1 | Number | Size of Descriptor in Bytes (9 Bytes) |
| 1 | bDescriptorType | 1 | Constant | Interface Descriptor (0x04) |
| 2 | bInterfaceNumber | 1 | Number | Number of Interface |
| 3 | bAlternateSetting | 1 | Number | Value used to select alternative setting |
| 4 | bNumEndpoints | 1 | Number | Number of Endpoints used for this interface |
| 5 | bInterfaceClass | 1 | Class | Class Code (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 6 | bInterfaceSubClass | 1 | SubClass | Subclass Code (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 7 | bInterfaceProtocol | 1 | Protocol | Protocol Code (Assigned by USB Org) |
| 8 | iInterface | 1 | Index | Index of String Descriptor Describing this interface |
QEMU struct DescConfig definition
struct USBDescIface {
uint8_t bInterfaceNumber;
uint8_t bAlternateSetting;
uint8_t bNumEndpoints;
uint8_t bInterfaceClass;
uint8_t bInterfaceSubClass;
uint8_t bInterfaceProtocol;
uint8_t iInterface;
uint8_t ndesc;
USBDescOther *descs;
USBDescEndpoint *eps;
};
Example (USB webcam : ususb -v)
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 14 Video
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Video Control
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 2 WebCam SC-13HDN10939N
Endpoint Descriptors
bEndpointAddress indicates what endpoint this descriptor is describing.
bmAttributes specifies the transfer type. This can either be Control, Interrupt, Isochronous or Bulk Transfers. If an Isochronous endpoint is specified, additional attributes can be selected such as the Synchronisation and usage types.
wMaxPacketSize indicates the maximum payload size for this endpoint.
bInterval is used to specify the polling interval of certain transfers. The units are expressed in frames, thus this equates to either 1ms for low/full speed devices and 125us for high speed devices.
Endpoint descriptors are used to describe endpoints other than endpoint zero. Endpoint zero is always assumed to be a control endpoint and is configured before any descriptors are even requested. The host will use the information returned from these descriptors to determine the bandwidth requirements of the bus.
| Offset | Field | Size | Value | Description |
| 0 | bLength | 1 | Number | Size of Descriptor in Bytes (7 bytes) |
| 1 | bDescriptorType | 1 | Constant | Endpoint Descriptor (0x05) |
| 2 | bEndpointAddress | 1 | Endpoint | Endpoint Address Bits 0..3b Endpoint Number. Bits 4..6b Reserved. Set to Zero Bits 7 Direction 0 = Out, 1 = In (Ignored for Control Endpoints) |
| 3 | bmAttributes | 1 | Bitmap | Bits 0..1 Transfer Type
01 = Isochronous 10 = Bulk 11 = Interrupt Bits 3..2 = Synchronisation Type (Iso Mode)
01 = Asynchronous 10 = Adaptive 11 = Synchronous
01 = Feedback Endpoint 10 = Explicit Feedback Data Endpoint 11 = Reserved |
| 4 | wMaxPacketSize | 2 | Number | Maximum Packet Size this endpoint is capable of sending or receiving |
| 6 | bInterval | 1 | Number | Interval for polling endpoint data transfers. Value in frame counts. Ignored for Bulk & Control Endpoints. Isochronous must equal 1 and field may range from 1 to 255 for interrupt endpoints. |
QEMU struct DescConfig definition
struct USBDescEndpoint {
uint8_t bEndpointAddress;
uint8_t bmAttributes;
uint16_t wMaxPacketSize;
uint8_t bInterval;
uint8_t bRefresh;
uint8_t bSynchAddress;
uint8_t is_audio; /* has bRefresh + bSynchAddress */
uint8_t *extra;
/* superspeed endpoint companion */
uint8_t bMaxBurst;
uint8_t bmAttributes_super;
uint16_t wBytesPerInterval;
};
Example (USB webcam : ususb -v)
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x87 EP 7 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 8
Ref: http://www.beyondlogic.org/usbnutshell/usb5.shtml#DeviceDescriptors
